10 Side Effects of Kidney Disease
What is Kidney Disease?
Renal disease, or nephropathy, can have various complications and side effects, especially if it progresses to advanced stages. A kidney disease’s underlying cause and severity can influence its specific side effects. The following are some of the common complications and side effects of kidney disease under the expert guidance of the best kidney specialist in Jaipur, Dr Ravi Gupta.
10 Side Effects of Kidney Disease in Your Body
- Fatigue: Kidney disease can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a reduced number of red blood cells or a lower concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen to the body’s tissues. Anemia in kidney disease results in reduced oxygen-carrying capacity, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Kidney disease can contribute to high blood pressure (hypertension) through various mechanisms. The kidneys play a key role in regulating blood pressure, and when they are damaged, this regulation can be disrupted. In turn, high blood pressure can further damage the kidneys, creating a harmful cycle.
- Fluid Retention: Impaired kidney function may result in the body’s inability to regulate the balance of fluids effectively. This can lead to fluid retention, causing swelling (edema), typically in the legs, ankles, or face. The accumulated fluids are not properly excreted by the kidneys.
- Proteinuria: Kidney damage can cause the loss of protein in the urine, a condition called proteinuria. Normally, the kidneys filter waste products from the blood while retaining essential proteins. When proteins are lost in the urine, it can lead to further health problems and contribute to the development of edema.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Kidneys are responsible for maintaining the balance of various electrolytes in the body, including potassium, sodium, calcium, and phosphate. Kidney disease can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to electrolyte imbalances, which can have various adverse effects on the body, such as muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, or weakness.
- Metabolic Acidosis: Kidney disease can result in the accumulation of acid in the body, leading to a condition known as metabolic acidosis. This can affect various organ systems, leading to symptoms like confusion, rapid breathing, and muscle weakness.
- Bone and Mineral Disorders: The kidneys are crucial for maintaining the proper levels of calcium and phosphate in the body. Kidney disease can disrupt these balances, leading to bone and mineral imbalances, including bone weakening. This condition is known as renal osteodystrophy and can result in fragile bones.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Kidney disease is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attacks and heart failure. The mechanisms involved in this association are complex but can include factors like high blood pressure and inflammation.
- Neurological Symptoms: In advanced kidney disease, the accumulation of waste products and electrolyte imbalances in the body can affect the nervous system. This can lead to symptoms such as confusion, difficulty concentrating, and even seizures.
- Itching (Pruritus): The buildup of waste products in the blood, such as urea and creatinine, can lead to severe itching of the skin, a condition known as pruritus.
Some More Side Effects of Kidney Disease
- Anemia: Kidney disease can lead to decreased production of erythropoietin, a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production. This can result in anemia, leading to fatigue, weakness, and paleness.
- Edema: Swelling in various parts of the body, especially in the ankles and legs, can occur due to fluid retention, a common consequence of impaired kidney function.
- Infections: Weakened immune function in individuals with kidney disease can make them more susceptible to infections. The kidneys filter waste and toxins, and when they don’t function properly, the immune system can be compromised.
- Kidney Failure: As kidney disease progresses, it can ultimately lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste and excess fluids from the body. At this stage, individuals may require dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive.
19 Other symptoms of kidney disease include
- Weight Loss and Poor Appetite: Kidney disease can lead to a decrease in appetite and unintended weight loss. This may be due to factors like the buildup of waste products and toxins in the body, altered taste perception, and hormonal imbalances.
- Swollen Ankles, Feet, or Hands: Swelling, also known as oedema, occurs when the kidneys cannot effectively remove excess fluid from the body. Fluid buildup can lead to swelling, often starting in the extremities, such as the ankles, feet, or hands.
- Shortness of Breath: Kidney disease can cause fluid to accumulate in the lungs (pulmonary oedema), resulting in shortness of breath. This occurs when excess fluid interferes with normal lung function.
- Tiredness: Fatigue and overall tiredness are common symptoms of kidney disease, often due to anaemia and the buildup of waste products in the bloodstream.
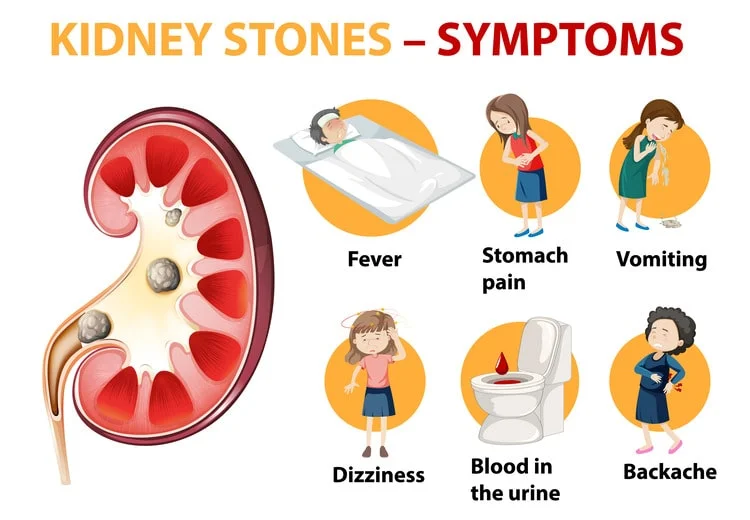
- Blood in Your Urine: Hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine and can be a sign of kidney disease. It can be caused by kidney infections, kidney stones, or other kidney-related issues.
- Increased Need to Pee, Particularly at Night: An increased urge to urinate, particularly at night, is known as nocturia. It can be caused by various kidney-related conditions, including impaired kidney function.
- Difficulty Sleeping (Insomnia): Kidney disease and its associated symptoms, such as itching, fluid retention, and frequent urination, can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia.
- Itchy Skin: The accumulation of waste products in the blood, such as urea, can lead to severe itching of the skin, known as pruritus.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting can be associated with kidney disease, particularly when waste products accumulate in the bloodstream. It can also be related to high blood pressure or electrolyte imbalances.
- Muscle Cramps: Electrolyte imbalances, especially low levels of calcium and potassium, can result in muscle cramps in individuals with kidney disease.
- Dry, Itchy Skin: Dry skin is a common complaint in kidney disease, and it can be exacerbated by the buildup of waste products and a lack of moisture in the skin.
- Urinating Either Too Much or Too Little: Changes in urinary habits are common in kidney disease. Some individuals may experience increased urination (polyuria), while others may produce very little urine (oliguria or anuria) due to impaired kidney function.
- High Blood Pressure: Kidney disease can lead to high blood pressure (hypertension) and is both a symptom and a risk factor for further kidney damage.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Kidney disease can make individuals more susceptible to urinary tract infections, which can lead to symptoms such as painful urination, frequent urination, and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Protein in Your Urine: Proteinuria, or the presence of excess protein in the urine, is a sign of kidney damage and can be an early indicator of kidney disease.
- Chest Pain or Pressure: Chest pain or pressure can occur in advanced kidney disease, often due to complications like heart disease or fluid buildup around the lining of the heart.
- Seizures or Coma in Severe Cases: In severe cases of kidney disease, when waste products and electrolyte imbalances are not properly managed, it can lead to neurological symptoms such as seizures or even coma.
- Fluid Buildup Around the Lining of the Heart: Pericardial effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the sac surrounding the heart (pericardium). This can occur in kidney disease due to fluid retention.
- Fluid Buildup in the Lungs: As mentioned earlier, fluid accumulation in the lungs (pulmonary oedema) can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath and can be a severe complication of kidney disease.
When to See a Urologist for Kidney Diseases:
You should see a urologist for kidney diseases if you experience persistent symptoms like blood in your urine, changes in urine colour, increased urination frequency, or painful urination. Additionally, if you have high blood pressure or diabetes, both of which can impact kidney health, consulting a urologist is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kidney disease poses a significant threat to overall well-being, as it can lead to a wide range of complications affecting various bodily systems. These complications encompass physical symptoms like fatigue, high blood pressure, fluid retention, and electrolyte imbalances, as well as emotional challenges such as itching and overall discomfort.
Kidney disease can progress to severe stages, ultimately leading to kidney failure and a need for dialysis or transplantation. Early detection and management of these side effects are crucial to enhance the quality of life for individuals with kidney disease and mitigate the risk of serious health issues associated with this condition.